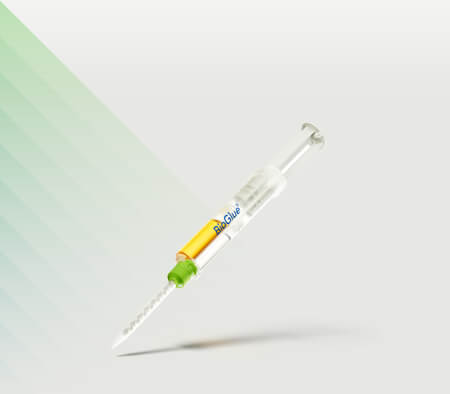
Advancing Aortic Technologies
with Purpose™







January 29, 2024
Artivion Announces Presentation of Late-Breaking Data from AMDS PERSEVERE Trial at the 60th Society of Thoracic Surgery Annual Meeting
Full IDE Data Set Demonstrates Statistically Significant Reduction of All-Cause Mortality and Primary Major Adverse Events (MAEs) at 30 days with use of AMDS in Acute DeBakey Type I (ADTI) Dissections Complicated by Malperfusion

November 9, 2023
Artivion Announces Completion of Enrollment in PERSEVERE Trial.
The PERSEVERE trial is a prospective, multicenter, non-randomized clinical trial to determine if patients with acute DeBakey Type I aortic dissection can be treated safely and effectively using the AMDS Hybrid Prosthesis.

October 5, 2023
Late-Breaking Science Presented at the 37th European Association for Cardio-Thoracic Surgery Annual Meeting
Artivion Announces Presentation of Real World Data from Post Market Study of On-X® Aortic Heart Valve Replacement Patients Treated with Low Dose Warfarin

October 5, 2023
Interim Data Demonstrate Meaningful Reduction of All-Cause Mortality with AMDS
Artivion Announces Presentation of Late-Breaking Interim Data from AMDS PERSEVERE Trial at the 37th European Association for Cardio-Thoracic Surgery Annual Meeting
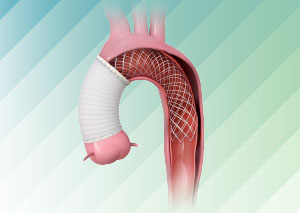
July 27, 2022
Artivion Initiates Enrollment in PERSEVERE Clinical Trial
Study Designed to Evaluate the Safety and Efficacy of the AMDS Hybrid Prosthesis to Treat Acute DeBakey Type I Aortic Dissections & Support U.S. FDA PMA Submission.

FDA Accepts CryoLife IDE Application for PERSEVERE Pivotal IDE Study
A Prospective, Single Arm, Multi-center Clinical Investigation, to Evaluate the Saftey and Effectiveness of AMDSTM in the Treatment of Acute DeBakey Type I Dissection
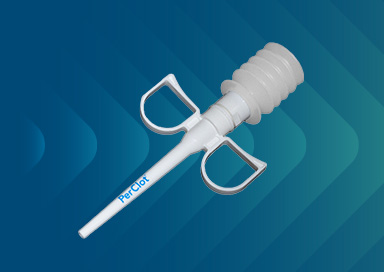
July 29, 2021
CryoLife Announces Sale of PerClot to Baxter
CryoLife Announces the Sale of PerClot to a subsidiary of Baxter International, Inc.

September 2, 2020
CryoLife Acquires Ascyrus Medical
CryoLife Acquires Ascyrus Medical LLC, Developer of AMDS Hybrid Prosthesis. Ascyrus is a Florida-based, privately-held developer of the Ascyrus Medical Dissection Stent (AMDS™), the world’s first aortic arch remodeling device used for the treatment of acute Type A aortic dissections.
When the need is aortic,
the solution is Artivion
Our intentional focus on the aorta and collaboration with the world’s foremost cardiac and vascular surgeons allow us to leverage our combined expertise in the development of new, innovative, life-changing aortic-centric technologies.
Please contact your local Artivion representative for details.
HEART VALVE
SOLUTIONS

ALLOGRAFTS
CARDIAC & VASCULAR

- CRYOVALVE® SG PULMONARY HUMAN HEART VALVE
- CRYOVALVE® AORTIC ALLOGRAFT
- CRYOPATCH® SG PULMONARY PATCH
- CRYOGRAFT® DESCENDING THORACIC AORTA
- CRYOARTERY® AORTOILIAC ARTERY
- CRYOARTERY® FEMORAL ARTERY
- CRYOVEIN® SAPHENOUS VEIN
- CRYOVEIN® FEMORAL VEIN
- CRYOVEIN® PC PEDIATRIC CONDUIT
- CRYOPATCH® AUTOLOGOUS PERICARDIUM
AORTIC ARCH
SOLUTIONS
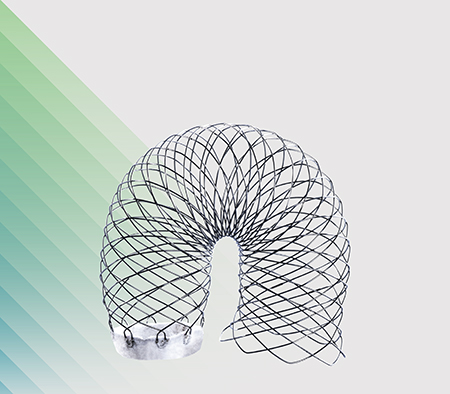
THORACOABDOMINAL
SOLUTIONS

ANCILLARY SOLUTIONS
CARDIAC & VASCULAR

Patient-Powered Progress
We provide solutions that have far-reaching impact on surgical outcomes and restoring the lives of patients fighting aortic diseases. Cardiac and vascular surgeons the world over—along with each patient in their care—have greatly benefited from our life-changing technologies.